About Stroke
The human brain is one of the most important organs in the body and is the most complex. It controls our speech, motor and sensory functions, vision, mood, behavior, memory, how we walk, breathing, coordination, heart rate function, and more. When the brain lacks nutrients to function, the damage may cause the rest of the body to function inadequately.
In the United States, stroke is one of the leading causes of death. The Center for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that approximately 795,000 people in the United States have strokes, and around 140,000 Americans die from stroke each year. A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that leads to the brain is partially or fully blocked (also known as an ischemic stroke) or bursts (hemorrhage stroke). This causes a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the brain tissue, leading to severe brain damage. Therefore, it is essential to keep the human brain healthy and stroke-free. The following information serves as a guideline for the signs, types, and treatment for common strokes. For further information and clarity, please contact Dr. Du or consult your neurologist.
Signs of stroke
● Sudden confusion, talking difficulty, or difficulty understanding speech
● Suddenly feeling numb or weak in the face, arm, or leg, especially on only one side of the body
● Sudden onset of a severe headache
● Suddenly having trouble seeing in one or both eyes
● Suddenly having trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination
Call 911 if you or you are noticing anyone experiencing these above symptoms. If your symptoms go away within 24 hours, you may have had a transient ischemic attack (TIA), and should contact your primary care physician as soon as possible.
Stroke Types
There are 3 types of stroke:
1. An ischemic stroke occurs when blood clots or other brain materials block the blood vessels to the brain. The subtypes of ischemic strokes are:
● Thrombosis: Thrombus formed in larger or small blood vessel
● Embolism: multiple acute strokes due to plaques from multiple possible sources
● Systemic hypo-perfusion
2. A hemorrhagic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel bursts in the brain. This may be due to:
● Hypertensive ICH
● Bleeding disorder
● Lobar or atypical hemorrhage – Amyloid angiopathy, bleeding into a tumor, vascular malformations, or drug use
3. Venous thromboembolism
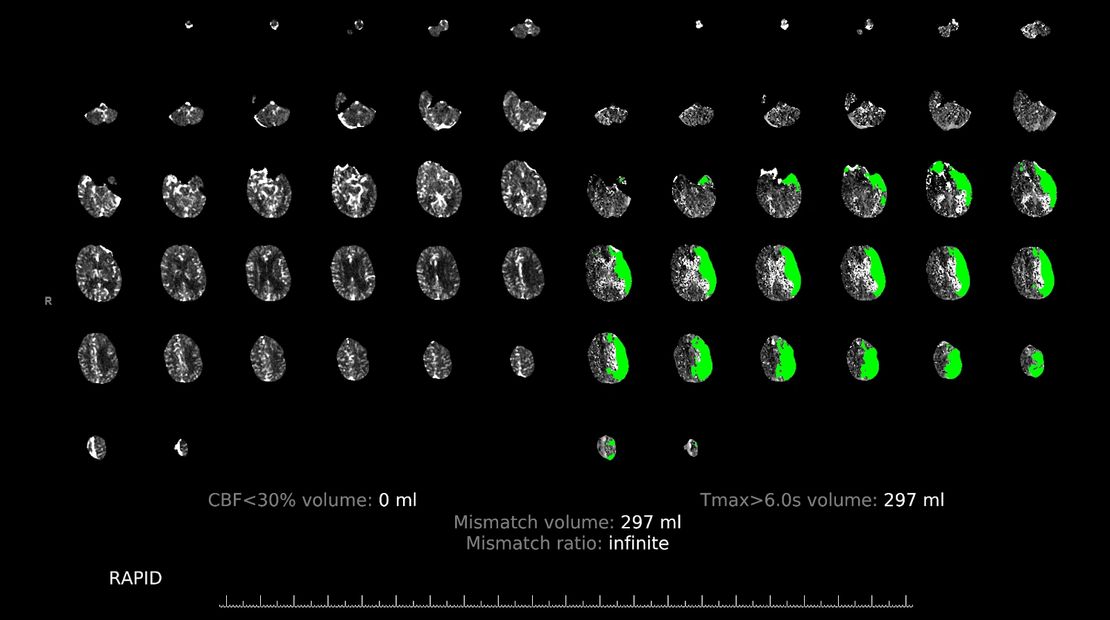
CT scan illustrating salvageable brain tissue with treatment in green. Obtained with patient consent.
Treatment for ischemic stroke
- Tissue plasminogen activator: (TPA/alteplase, which is used to dissolve blood) to start within 4.5 hours of symptom onset (Refer to the IV tPA Screening Checklist before tpa/thrombolytic therapy is started, the blood pressure should keep less than or equal to 180/105 mmHg for at least 24 hours).
- Mechanical thrombectomy within 24 hrs of symptoms onset if the patient has large vessel occlusion and rescuable brain tissue.
- Asa/Plavix within 48 hours of stroke onset, deep vein thrombosis, and aspiration prevention.
- Risk factors modification such as smoking/alcohol/atrial fibration (need anticoagulant if CHA2DS2 score > or = 1 in male and > or = 2 in female), diabetes ( the goal is less than 7% of HbA1c), uncontrolled Bp and cholesterol, exercise and/or weight loss if obesity, diet change if needed, and/or rehabilitation for illegal substance abuse.
- BP control.
- Ischemic stroke — if not treated with tpa, Bp should be treated if Sbp >220 mmHg or DBP >120 mmHg), But if pt has active CAD, CHF, aortic dissection, or pre-eclampsia/eclampsia, if treatment is indicated, then lower BP by 15 percent during the first 24 hours.
- Start treatment for HTN with > 140/90 in 24-48 hrs after onset stroke. The goal is to control Bp in a few days to a week. However, this is a different criterion if the patient has intracranial or extracranial artery stenosis.
- Start treatment HTN with SBp <130 with small vessel stroke.
- Start treatment HTN with S Bp <120 and help decrease any stroke by 41%.
- Blood pressure in acute hemorrhagic stroke.
- Lower Sbp less than 140 if Sbp 150-220.
- Lower Bp 140-160 if Sbp >220.
Treatment for transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Low-risk TIA, defined by an ABCD2 score <4. Start aspirin (162 to 325 mg/daily) alone.
- High-risk TIA, ABCD2 score ≥4, suggest using dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) using aspirin (160 to 325 mg loading dose, followed by 50 to 100 mg daily) plus clopidogrel (300 to 600 mg loading dose, followed by 75 mg daily) for the first 21 days.
- If the patient is on aspirin or clopidogrel at the time of TIA onset, we suggest aspirin plus clopidogrel for the first 21 days for high-risk TIA (an ABCD2 score of ≥4).
Stroke prevention
- Continuous telemetry, if no atrial fibrillation noted during the hospital stay, order outpatient 30-day cardiac event monitor if need
- Allow HTN (SBP up to 220) for the first 24-48 hours, then slowly achieve long term goal <140/90.
- A1C ( goal <6.5). diabetic education diet management.
- Lipid profile LDL (goal <70).
- Quit smoking/recovery program.
- Dietician referral, lifestyle intervention, nutrition, and weight management.
- Recommend engaging in regular physical exercise per therapy recommendations.
- Secondary Stroke Prevention is deferred to the primary team and primary care physician.
Copyright © 2025 Excellent Neurology - All Rights Reserved.